There was a time in our country’s history when farm-to-table wasn’t a trend, it was a necessity — especially when it came to dairy consumption.
If a family wanted milk, that milk came straight from the family’s cow and had to be consumed or turned into butter or cheese on milking day. Otherwise, it would spoil.
As farms and cities got bigger and fewer people kept their own cows, delivering fresh dairy became the milkman’s job. But the new process was far from perfect: Hand-delivered bottles were heavy and needed to be returned and sterilized, and without refrigeration, milk would still go bad within a day. Another problem: Glass jugs break.
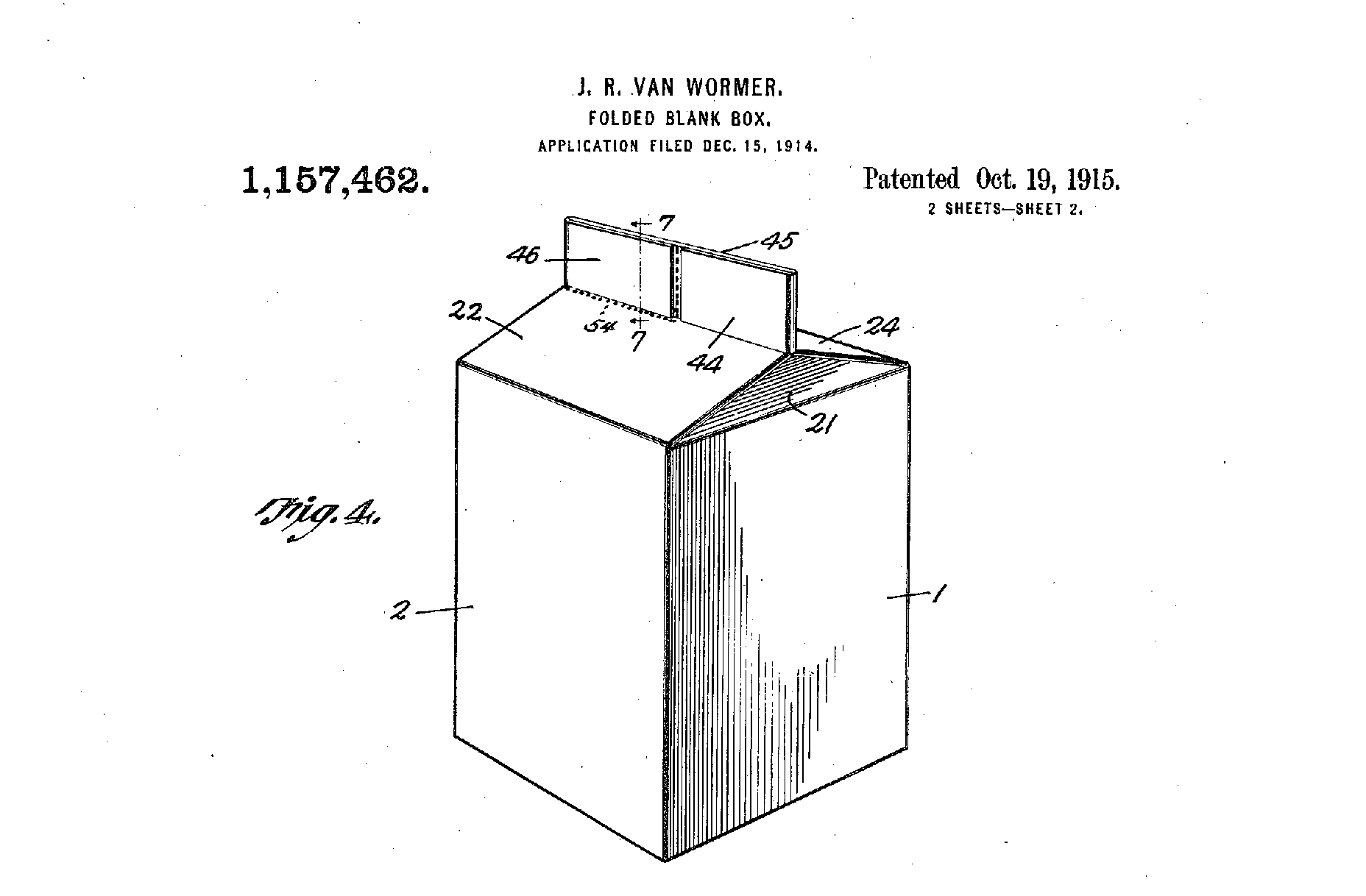
Legend holds that the inventor of the paper milk carton we know today dropped a glass jug one morning, sending milk and glass everywhere. In his frustration, John Van Wormer patented a paper milk carton that could be shipped flat and assembled as needed at the dairy. (Until this point, dairies used G.W. Maxwell’s earlier paper milk carton, which did not fold flat.)
Van Wormer’s early Pure-Pak milk cartons, patented in 1915, were made of paperboard and sealed with wax, which prevented the milk from saturating the paperboard. The gable-top closure helped maintain freshness during transport while eliminating the need for a cap. And unlike glass bottles, milk cartons were lightweight and disposable: They could travel farther and didn’t need to come back.

JOHN R. VAN WORMER
Although G.W. Maxwell gets credit for creating the gable-topped milk carton, toy factory owner John Van Wormer invented a carton that could fold flat, a revolutionary efficiency in the milk chain.
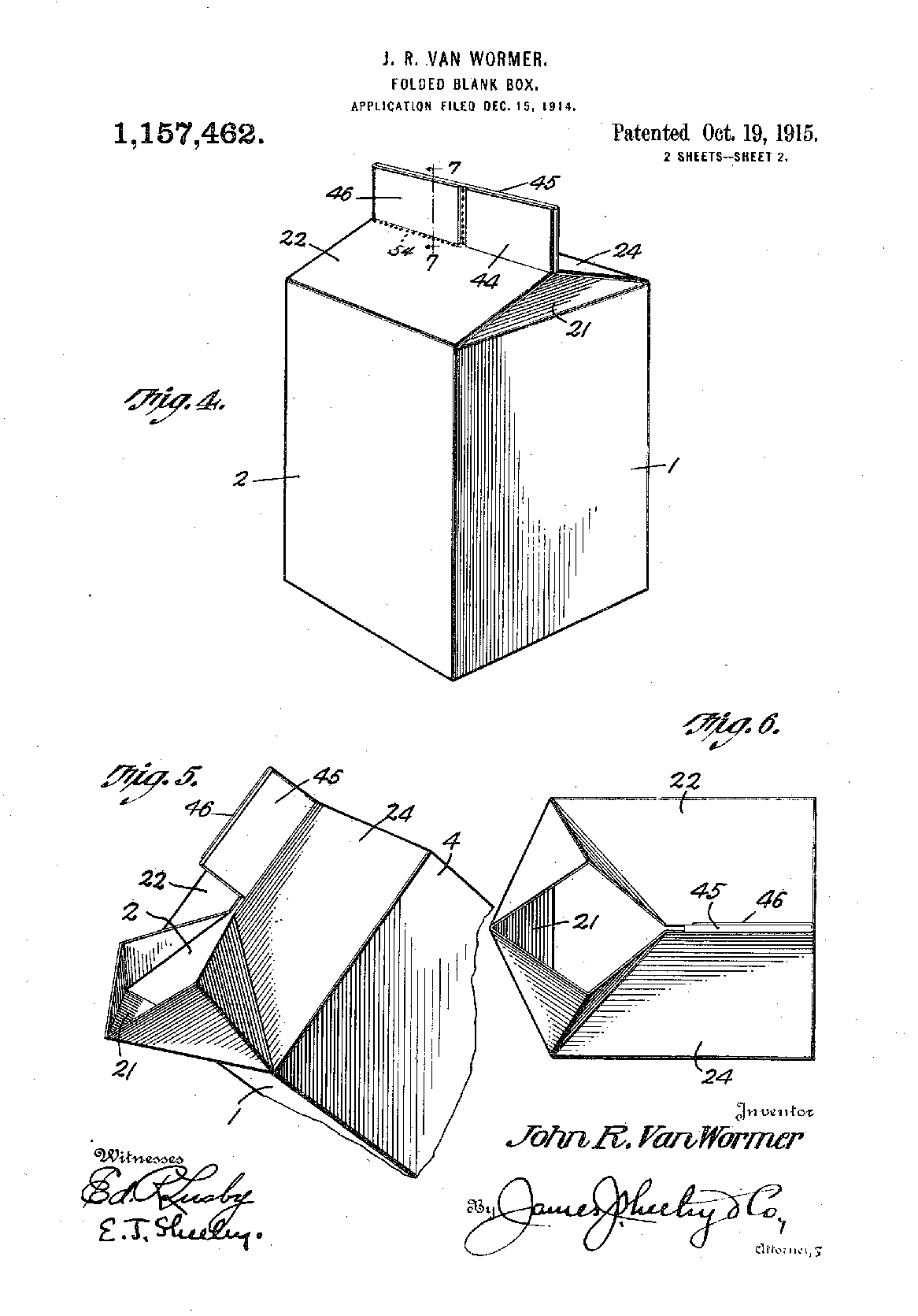
Patent drawing for milk container that could fold flat, invented by John R. Van Wormer.
While people had a hard time letting go of their beloved glass bottles, the coated carton slowly gained popularity, and as that transition began taking hold, so did refrigeration. By the late 1940s, electric refrigerators were in most American homes, small family-owned dairies were consolidating and the milkman was securing his Rockwellian role in the lives of American families and neighborhoods that soon became nostalgia.
While neither was necessarily dependent on the other, the milk carton, owes some of its success to advances in cold chain technology — a series of refrigerated tanks, trucks (“reefers”) — and storage units that ensure dairy and other perishables like meat and produce make it from the farm to the grocery store without spoiling.
Today, the value of cold chain markets that support perishable food distribution globally is estimated at around $250 billion. And while many countries lag in their cold chain facility development, the United States annually moves some three billion gallons of chilled milk through a cold chain so efficient that customers can buy refrigerated milk at nearly every gas station and corner store in the country.
As other countries expand their own cold chains, the U.S. cold chain industry stands to profit from rapid growth. According to the Global Cold Chain Alliance, refrigerated warehouse capacity around the world increased by 20 percent from 2012 to 2014, and three of the top five refrigerated warehouse operators are U.S. companies. But most of that milk is no longer being moved in Van Wormer’s carton: The milk carton may have solved the problem of breaking glass, but plastic jugs have overcome some shortcomings of cartons: They are less likely to leak and easier to re-seal.
According to Glen Harrington, director of manufacturing for the Borden Dairy Company, milk manufacturers were beginning to make their own gallon and half-gallon plastic jugs by the 1970s. When produced on a large scale, Harrington says, it’s more cost effective for dairy companies to make cartons in-house than it is to buy them.
Paperboard milk and cream cartons are still in use, but these days, they’re lined with polyethylene, a plastic used for food-safe packaging. In many countries outside the U.S., milk is sold unrefrigerated in shelf-stable cartons, like the ones used stateside for soups and broths. The milk is usually pasteurized at a higher temperature to extend shelf life. The downsides to this type of shelf-stable milk, according to Harrington, are that it typically costs more and doesn’t taste as good.
“We’ve got a good system,” says Harrington. “Why would we spend more to make it taste worse if we could just move it around fresh?”

PLASTIC MILK JUG
The design of plastic milk bottles evolved quickly in the mid-1960s, when the handled jug as we now know it was invented. The design not only saved dairies money, it encouraged customers to buy a gallon of milk at a time, a large amount compared to the smaller quantities sold outside the U.S.
Author
Emily Farris is a food writer, designer and stylist who freelanced for 10 years before co-founding Feed Me Creative, a culinary content studio in Kansas City, Missouri. She and her husband, Kyle, have a dog, six backyard chickens and a really nice whiskey collection.