What do you need in a bomb shelter? Water, flashlights, blankets, a radio and, of course, canned food.
In the 1950s and early 1960s, many a family fallout shelter was stocked with canned food, including Multi-Purpose Food (MPF), a low-cost, shelf-stable, protein- and nutrient-rich food supplement manufactured by General Mills to be consumed “in case of emergency or disaster.” MPF, first conceived in the 1940s as a remedy for widespread hunger in postwar Europe, became a symbol of Cold War preparedness.
Since the mid-20th century, canned food has been a staple of the American diet. According to the Can Manufacturers Institute, the average American household has 24 cans of food in their pantry. And while the technology of canned food focuses on creating a shelf-stable product, the significance of canned food in food culture is anything but fixed.
For as long as people have moved food from its production location to market, packaging has played a key role, from product durability and trade efficiency to product differentiation and marketing. Canned food — durable, stackable and completely sealed — has transformed multiple links along the food supply chain since its first appearance nearly 250 years ago. Military campaigns, with their widely distributed provisioning requirements, have often led to innovations in the processing, packaging and distribution of food, particularly sources of protein. Credit goes to the Dutch Navy for being the first, in the late 18th century, to package hot beef covered with hot fat in tinned iron canisters.
The first to publish on the process of canning — preserving food in sealed containers — was Frenchman Nicolas Appert in 1809, writing about a technique using glass containers. Fellow Frenchman Phillipe de Girard devised a canning process using tin and collaborated with Englishman Peter Durand, who obtained a patent in 1810. Durand promptly sold the patent to the British company Donkin, Hall and Gamble, which provided meat in tinned wrought-iron cans for the British Army and Royal Navy.
CONTAINER MATTERS
Now a pantry staple, canned food was initially conceived for use beyond a conventional kitchen. Metal cans could function as a serving container and, in a pinch, be heated over open flame. The sealed and opaque quality of the container prevented oxygen and light from breaking down food and protected it from contamination, thereby extending the product’s shelf life. Advances in metallurgy eventually helped cans become the cost-effective, disposable food containers now commonplace in kitchens and pantries.

 MULTI-PURPOSE FOOD (MPF)
MULTI-PURPOSE FOOD (MPF)
a low-cost, shelf-stable, protein- and nutrient-rich product made by General Mills for use in “emergency or disaster.”
Cans are easily stacked and difficult to destroy, criteria that make them indispensible to military food supply chains. Contents can be cooked right inside the can, offering the prospect of a warm meal to anyone with access to a flame.
Three types of metals are now commonly used for cans. Tinplate is made by coating steel with a thin layer of tin, which is highly corrosion resistant. Cans made of aluminum — corrosion resistant and highly malleable — can be fabricated from two rather than three pieces. Electrolytic chromium-coated steel (ECCS, also known as tin-free steel), introduced in the 1960s to respond to fluctuations in the supply and cost of tin, has a higher melting point than tinplate but is less resistant to corrosion.
As the fabrication processes for rolling, shaping, soldering and welding metal improved, so did cans. They became thinner and more durable. Sealing methods evolved, too — some early cans were soldered closed with lead. A firmer understanding of microorganisms also has changed canning practices. Botulism from commercially produced canned food is now a rarity. Sustained high heat in processing kills spores of the Clostridium botulinum bacterium, which can otherwise survive in low-oxygen environments.
Opening metal cans initially required brute force and assumed the availability of heavy tools. The first metal can openers weren’t patented until the 1850s — some 50 years after the container itself came into use. Subsequently, market expansion led to the engineering of new opening strategies, which in turn made cans increasingly popular. Key-wind opening systems, which include a key with which to pull away a strip of metal (usually on the top of a can or tin), and later, easy-open ring tabs, made for portable, pocket-sized, accessory-free foodstuffs.
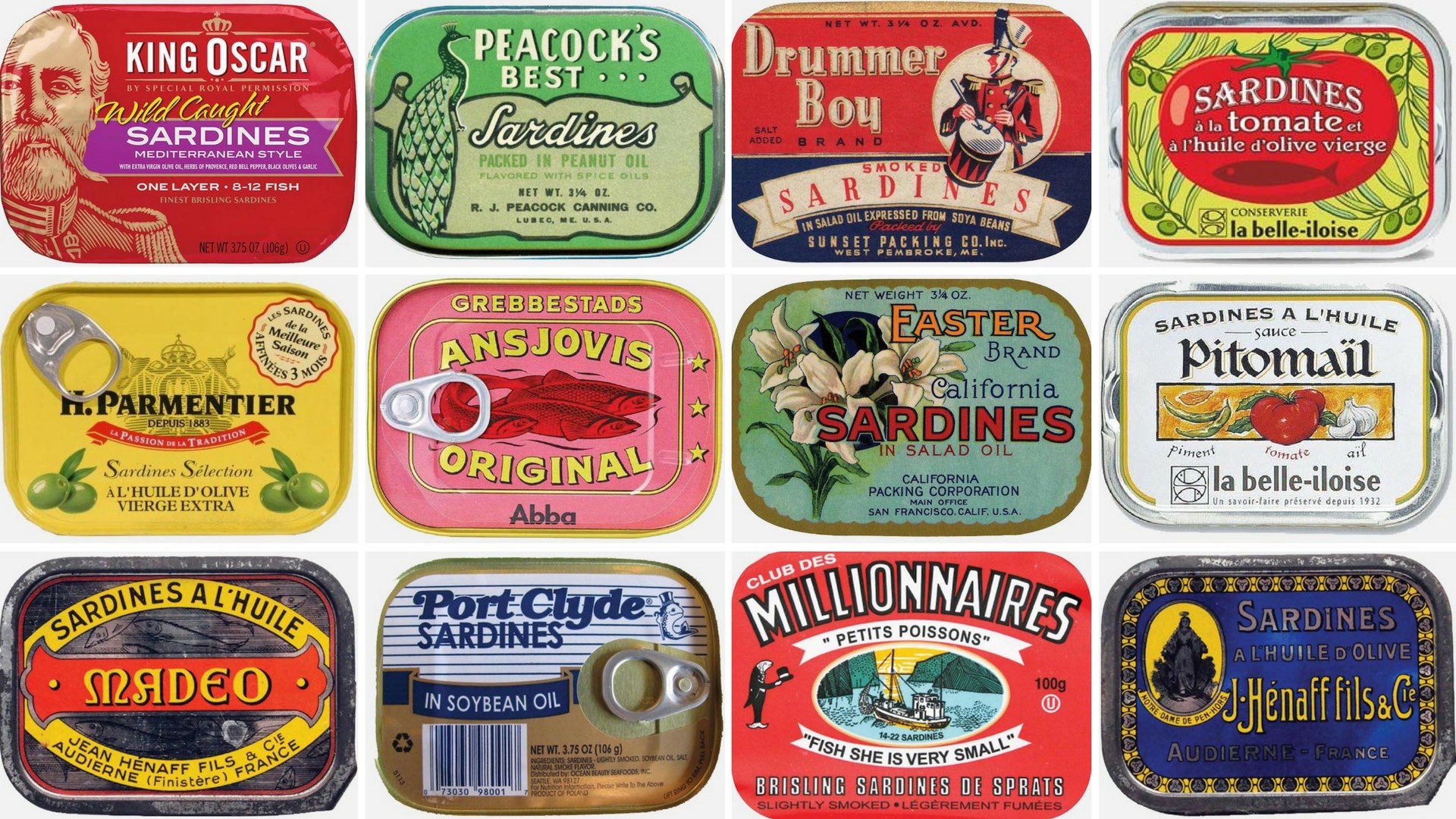
Like other products now considered relatively common, such as chocolate, 19th-century canned food took on special significance for a growing middle class. Take, for instance, ready-to-eat seafood “delicacies.” Comparable to predecessors such as salt cod and pickled herring, seafood cooked (or smoked) and packed in cans or tins offered a way to expand the market for seafood harvested in a specific location.
Canned sardines are but one example of a product that emerged as a delicacy and then became a crucial wartime ration during the two world wars. At its peak in 1939, the central California fishery associated with Cannery Row in Monterey landed 460,000 tons of sardines for the year. Today, canned sardines and anchovies, as well as other canned seafood products, cover a broad market range, from in-house brands for major supermarket chains to restaurants offering carefully selected tinned fish delicacies.
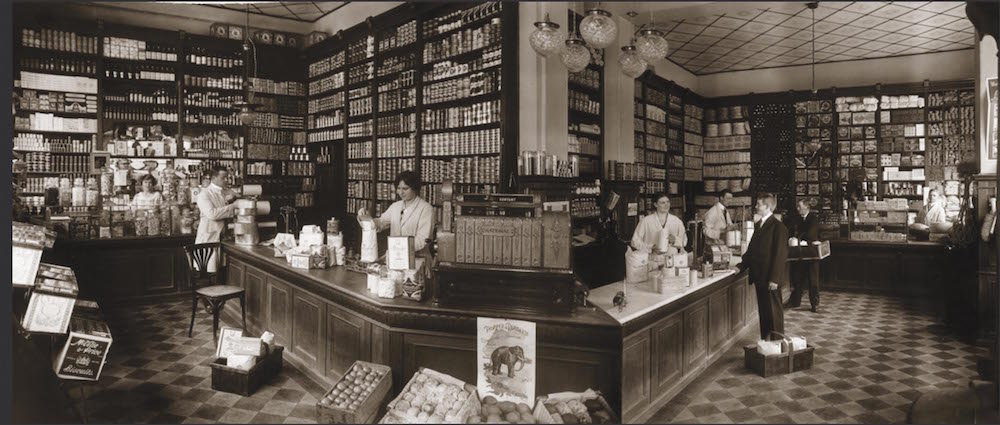



Before canned food, groceries were full-service stores, where grocers measured and gathered your order together. Prepackaged cans, with labels as built-in advertising, enabled consumers to choose and pick up goods themselves.
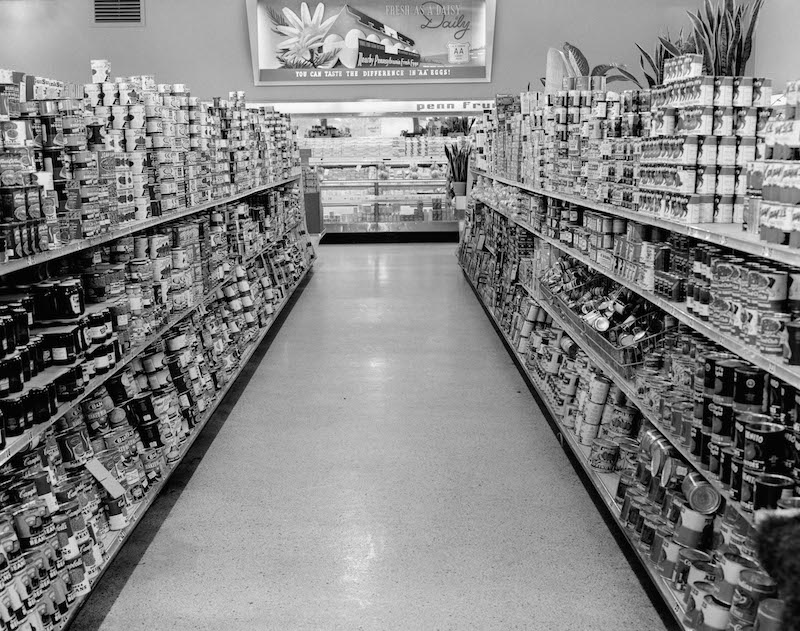

In 1917, the Piggly Wiggly market chain opened the first self-service grocery in Memphis, moving cans out from behind the counter into displays, and then shelves. This image is from the mid-1950s.
THE ART OF THE SELL
Food science and packaging technology created canned food, but grocers introduced it to the American household. Canned food transformed the role of grocers as well as the design of stores. As a prepackaged good of consistent weight, with labels as built-in advertising, canned food could practically sell itself. In 1917, the Piggly Wiggly market chain opened the first self-service grocery in Memphis, moving cans out from behind the counter into displays, and then shelves, where consumers could pick up cans, read labels and put them into carts. After World War II, the housing boom, the expansion of supermarkets, the practice of driving to shop for groceries, and the greater number of women working outside the home all helped normalize canned food as part of the modern American diet.
Artful labeling and package design is an integral part of branding, particularly for products sold in opaque containers. The rounded corners of rectangular metal tins of fish are practical, as well as emblematic of product contents. Streamlined form and graphic design evoke a sense of efficiency. Many original label motifs persist as recognizable brands today. In 1962, Andy Warhol painted the first of his Campbell’s cans series — 32 paintings that represent each offering in the Campbell’s brand — elevating the Campbell’s soup can into Pop Art.

The most money ever paid for a can of soup was $11.7 million for Andy Warhol’s Small Tom Campbell Soup Can (Torn Pepper Pot), one of 32 paintings in his soup can series, first exhibited in 1962.
NUTRITION: IS IT IN THE CAN?
In 1990, Congress passed the Nutrition Labeling and Education Act (NLEA) requiring all packaged food to list nutritional information relative to Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA). For the first time, consumers could compare the nutritional content of foods before buying them. Since then, processing improvements have enabled the use of fewer preservatives and increased nutrient retention. Nutrition research has also been important, for instance, in clarifying that canned fruits and vegetables do not make up a major source of sodium in the American adult diet.
For many people, canned food is a more nutritious choice than other food options, especially when accounting for seasonal availability. New packaging technologies — such as bisphenol A (BPA)–free see-through plastic cans now coming on the market — prompt the question: Does being able to see what’s in the can ensure that it is fresh, flavorful and healthy? The market will decide.
From newfangled packaging for military rations to convenience-food wonder for postwar households, the simple can ensured that foods grown or produced in one location could safely be consumed many hundreds of miles away. And while its status may have ebbed and flowed — from nifty new technology to cheap holder of less-than-fresh ingredients, and back to retro packaging of exotic delicacies — canned food remains a staple for pantries and fallout shelters the world over.
 Need a refresher on how to play Kick the Can? Check out this helpful video.
Need a refresher on how to play Kick the Can? Check out this helpful video.


Author
Laurie Zapalac is the founder of Zapalac Advisors, a Boston-based urban planning firm providing research and strategic planning for urban revitalization and enhancement. Laurie is passionate about understanding how and why digital technology is making historic urban environments newly attractive as places to live, work and play. When not traveling farther afield, you can find her trekking the New England coastline and enjoying local bakeries.