The Freshest Leafy Greens
Have you ever had a salad with lettuce freshly picked from the garden? Maybe your grandmother grew her own greens, or perhaps that farm-to-plate restaurant you love makes amazing salads. Unless you have your own backyard garden, fresh lettuce most likely travels the distance from the farm to your grocer on a long-haul truck. Until now.
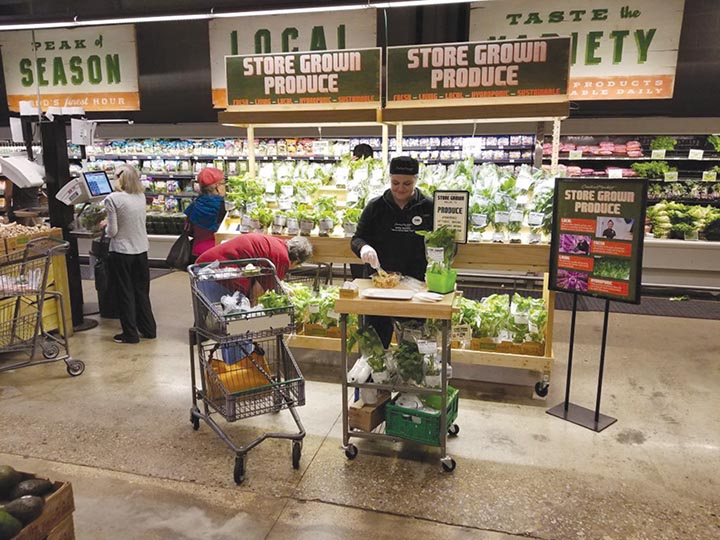
A 21st-century lettuce farm no longer requires muddy rows cut into a rural field subject to the whim of weather and labor. Behind a suburban grocery store in Dallas, fresh leafy greens are produced under a limitless pink glow inside a clean, 53-foot-long, steel shipping container, yards away from where they will eventually be sold.
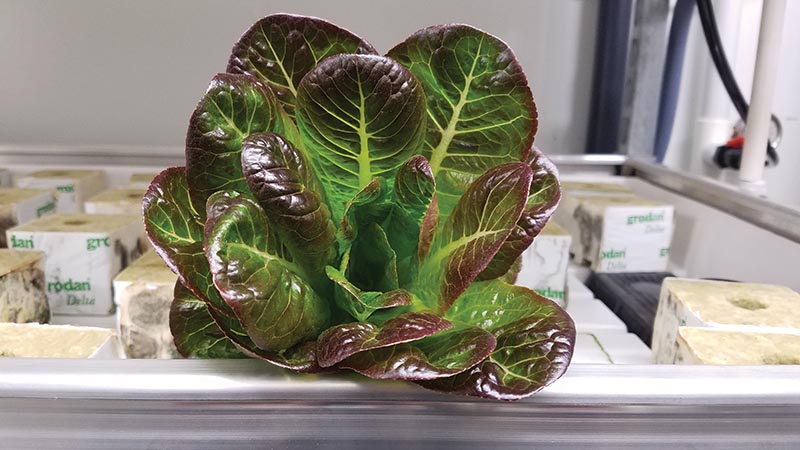
The glow — provided by LED lights in both the red and blue spectra — is an engine that works 24-7, producing spicy arugula rich in vitamins and antioxidants, fresh green leaves ruffled in purple and romaine so crisp that it oozes milky sap when cut.
Since May 2017, Central Market, the gourmet offspring of the family-run, Texas-based H-E-B Grocery Co., has been selling lettuce and herbs grown on-site. Production is contained and perfected so that customers have access to a daily harvest of fresh, organic greens. While Austin-based rival Whole Foods has partnered with another company to sow seeds on a store’s roof, and startups like San Francisco’s Plenty have built large urban food-production facilities, Central Market’s growing container represents the first time that a grocery store has grown produce on-site with their own staff.
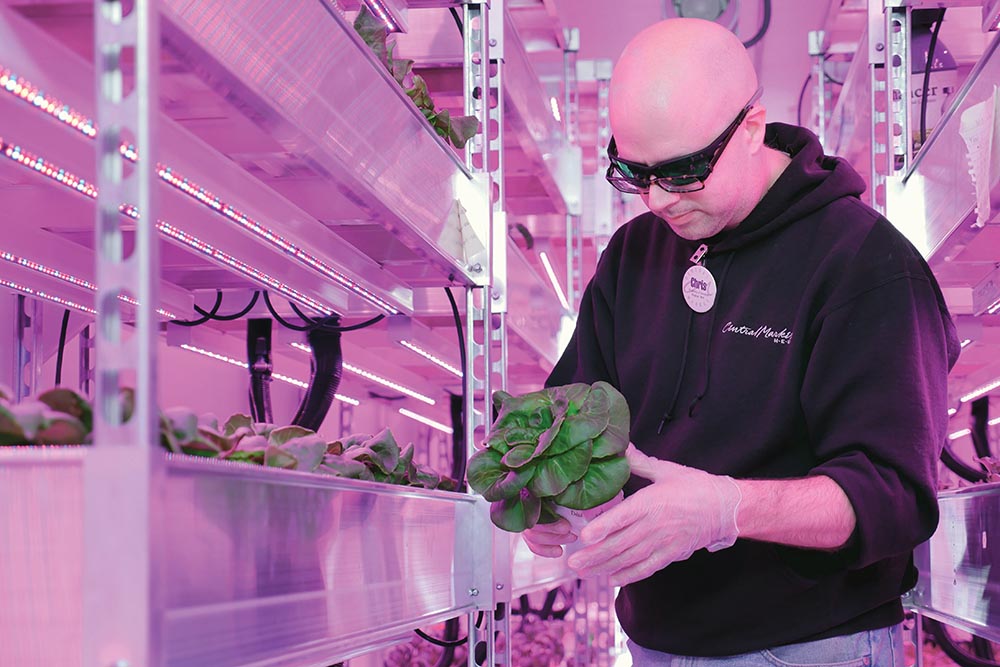
The container garden is the brainchild of Marty Mika, produce specialist and buyer for Central Market. After years of working to procure the freshest ingredients for customers, he is well aware of how difficult it is to always have the best on hand.
“There are so many variables in produce: Mother Nature, seasonality, labor issues, water and even transportation,” says Mika. “So, we looked at how we could take over some of the supply chain and put all of these issues under our own umbrella.”
Americans eat a lot of lettuce — about 11 pounds of romaine and other leafy lettuces per person per year, and even more if hardy iceberg varieties are considered. In 2017, romaine and other leafy green harvests were valued at over $2 billion, a substantial increase in value from the previous year. Salad, a key component of a healthy diet, is so popular that many fast-food chains have added salads to their menus. At-home salad consumption is increasing too, thanks partly to new packaging in bags and clamshells that can extend freshness.
But getting lettuce to the table at the peak of perfection is not an easy task. The challenges are numerous: drought, pests, temperature, contamination and physical damage during transportation.
Lettuce is a cool-weather crop, so it grows best when days are not too hot and nights are not too cold. Because of this, 90 percent of all romaine and leafy greens harvested in the U.S. hail from either California or Arizona. As a result, much of the lettuce produced travels great distances to end up plated with a tomato and vinaigrette.
The transportation challenge means that lettuce is often picked just before maturity and immediately bundled onto a truck for distribution. Driving lettuce to markets adds to the cost of food, especially when fuel costs fluctuate. A 2013 USDA report found that a doubling of diesel prices could lead to an average increase of 20 to 28 percent in wholesale prices for a variety of produce.
Another issue related to transportation is nutrient loss. Research has shown that as lettuce is trucked across the country from farm to market, levels of ascorbic acid, chlorophyll, carotenoids and important minerals decrease, a reduction in quality that persists as long as the lettuce is being moved or sits on a shelf in a supermarket before purchase. Transportation also introduces new risks into the food chain: If vehicles are not adequately cleaned and maintained, there is always the potential for contamination.
So, what is a purveyor of produce to do?
Contain. Contain. Contain.
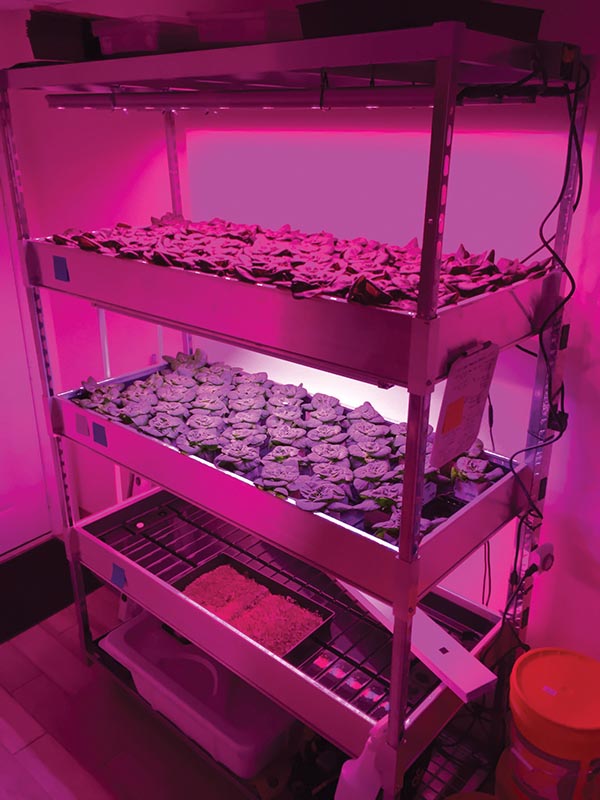
To facilitate growing their own fresh greens, Mika and his Central Market team purchased a domestic shipping container from Growtainers that had a few modifications crammed into nine feet of headspace: neat units with four shelves, a system for modulating temperature and an LED growing system that shines 24 hours of pink light into every corner. The crop grows in a perfectly controlled environment primed for maximum production.
In Dallas, Central Market employees sow varieties of lettuce and herbs into a medium made of melted rocks. This clean, sterile substrate is the perfect underpinning for growing plants hydroponically, or without soil. Nutrients are added to the water, and the plants grow rapidly without pesticides or herbicides. In addition, the temperature range in the container can be optimized for growth. And though scientific research has not shown that pink light makes plants grow more quickly, the LED system that uses only some wavelengths of the light spectrum allows plants to flourish while saving on energy costs.
Many commercial hydroponic growers do not want to talk about proprietary data and results; however, research suggests that crops can be coaxed to grow between 20 and 50 percent faster in hydroponic conditions. Recent research also shows that hydroponic farming can yield 11 times as much lettuce per area under cultivation and uses a fraction of the water when compared to conventionally farmed lettuce.
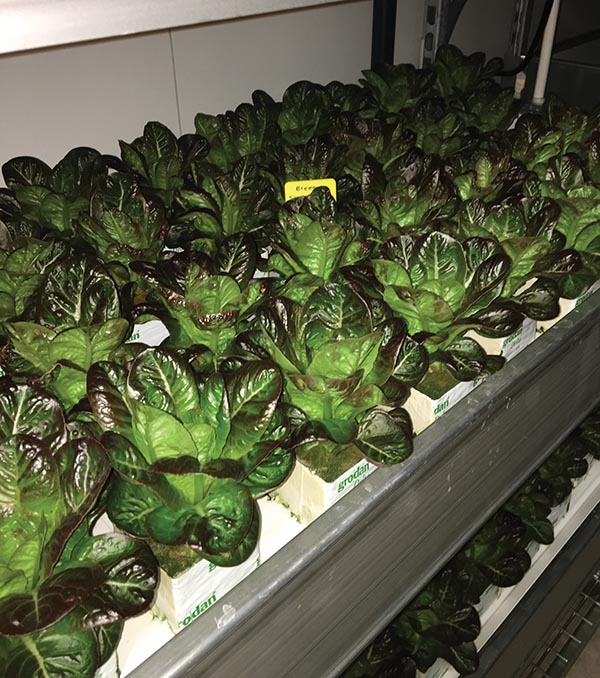
The Dallas team plants and harvests by section within the container. Each new planting takes over a new set of shelves, which enables a scheduled harvest of perfect greens to be plopped into a clamshell and then moved to the market shelf in minutes. The work is very detail oriented, but once the process starts, it is consistent and easy to maintain.
Even better: Transportation of product to retailer is now a mere few feet, and customers have access to pesticide-free, organic produce.
“We produce enough of different, basic varieties each week to sell in the store: not too much, not too little,” said Mika. “Customers like the flavor and freshness of the greens, and they like the fact that we’re reducing the carbon footprint.”
There are some disadvantages to producing container lettuce, though, including high initial costs for equipment. In addition, because container farms tend to be in urban areas — close to customers — the cost of land is high. These costs are passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices for greens. Hydroponic farming also uses much more energy than conventional farming — more than 80 times the amount of energy, although this excludes energy used for transportation.
Stay tuned. Researchers are developing more sustainable practices for indoor farming that should further reduce the carbon footprint.