Handoffs: Bills of Lading and the Cargo Custody Relay
We’re hearing more and more about high-tech ways to track and trace our food as it moves through the supply chain to our plates — from barcodes to blockchains. But the practice of tracking food shipments isn’t new. It has long been a way for shippers to make sure their cargo is safe and secure throughout its voyage.
At each step along the supply chain, anyone who handles a shipment has custody, a specific term that connotes legal responsibility. The chain of custody confirms the identity and quantity of the shipment (e.g., 400 bushels of Italian pears), declares that the pears were continuously controlled and transported by the carrier and identifies everyone who handled the pears throughout the shipment. Having a clear record of this chain makes it possible for the shipper to track any theft or contamination of the cargo on its way to the receiver.
The documentation that authenticates the movement of food between a shipper and a freight carrier is known as a bill of lading. It’s a receipt that confirms the transition of goods from one link in the chain to the next. This document notes the details of the cargo and its intended path to you, including the type and quantity of a shipment. It’s provided at the end of a shipment to verify delivery of the goods shipped and is the basis for payment for the goods at the receiving end of a shipment. Without these bills of lading, neither the farmer nor the exporter gets paid.
Going back to maritime practices — before planes, trains and automobiles got involved — the bill of lading would have been prepared by a merchant to indicate that the shipper was responsible for delivering the items consigned to him. These receipts were originally called “bills of loading” as far back as the Middle Ages, and they listed what a merchant actually loaded onto a ship. It was a sort of contract between a merchant and a shipper that confirmed the receipt and safe transport of a specific cargo list.
Since shippers often lost ships and their cargo at sea, the bills of lading helped account for losses and reparations. Like today’s tracking tools, bills of lading indicate a transfer of responsibility throughout the supply chain. They are legal documents that confirm ownership of the goods and, as such, are assets the shipper can use to secure credit against expenses.
As the bill of lading moves through the supply chain with a shipment of, say, bags of coffee beans on pallets, the legal notion of ownership and custody travels with the chain. But the cargo list and a receipt are only two tools that leave footprints along a supply chain. These days, we need much more data than these documents provide to effectively track food through our chain.
Newer tools include smart labels with barcodes that communicate harvest dates and times. Scans of smart tags indicate precisely when food passes through the supply chain, when a USDA inspector has certified a meat shipment or the temperature of the interior of a shipping container or a tractor trailer. All this data is being gathered as food travels to our plates.
These new tools go far beyond those old bills of lading, but the intention of those bills and the chain of custody remain the same.
Just wait until blockchain technology picks up where bills of lading and custody left off. Then you’ll be able to see the passage of ownership of your carrots all the way from the farmer’s plot to your pot, who handled your carrot and why, when, where and maybe even the weather outside when the carrots moved between buildings. Be prepared for some surprises.
Blockchain Explained
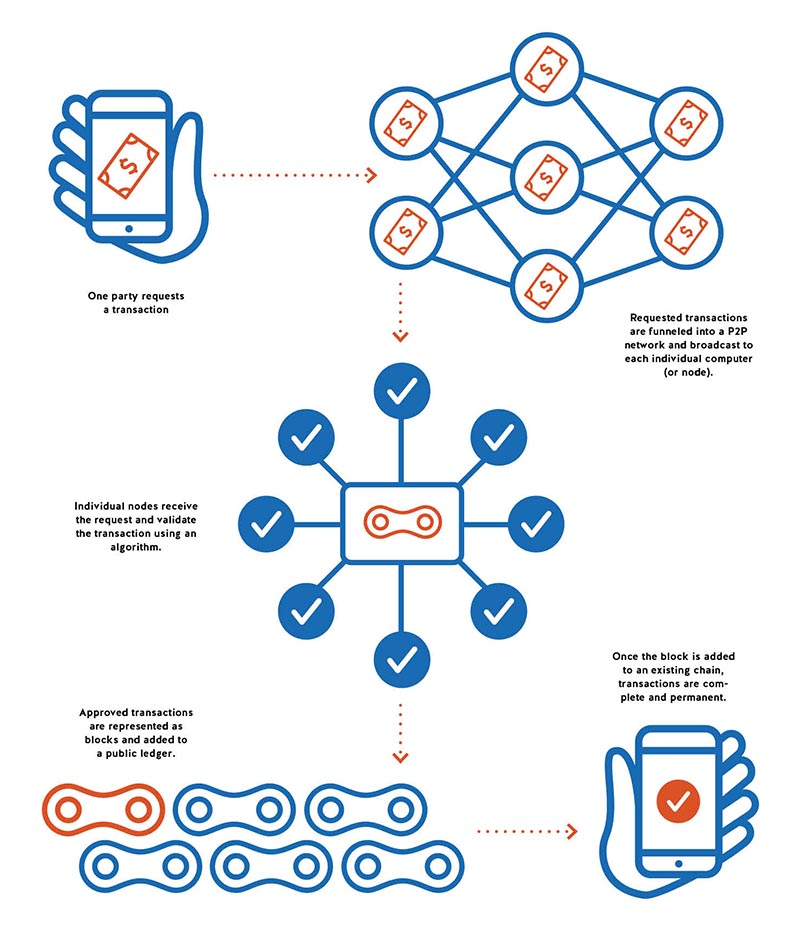
A blockchain is a distributed, digital ledger used to track shipments. Rather than a single document — the old bill of lading — traveling throughout a supply chain, the information contained in that one document exists in many computers in the network along the way. So every time a bushel of apples moves through its supply chain, information about its steps are recorded, including who moved it, when, why and what resulted from the movement. The data form blocks that leave unique “fingerprints” along the chain. Any attempt to change a fingerprint travels throughout the entire chain, alerting everyone that the integrity of the chain was compromised. If someone steals an apple, the blockchain will know where and when it disappeared. For the food industry, blockchain appears to be a way to prevent food fraud and ensure food safety. Real-time awareness of inconsistencies in the chain will enable faster and more precise responses to food-borne disease outbreaks. Consider the Romaine lettuce contamination in early 2018. Blockchains would have enabled investigators to track back all the way to rows of lettuce growing in the field. At least that’s the theory.


 Keep up with the latest in logistics entrepreneurship and follow Layla Shaikley on Twitter
Keep up with the latest in logistics entrepreneurship and follow Layla Shaikley on Twitter 




 Don’t be surprised when you begin to notice your sidewalk cluttered with electronics instead of people. DoorDash, an on-demand food delivery service based in San Francisco, is testing out robots as an addition to its food-delivery workforce. [Read more about DoorDash in our story, “
Don’t be surprised when you begin to notice your sidewalk cluttered with electronics instead of people. DoorDash, an on-demand food delivery service based in San Francisco, is testing out robots as an addition to its food-delivery workforce. [Read more about DoorDash in our story, “