Market System: The Case of Early New York
Petitioned in 1786 by prominent residents of New York City’s far-flung Catharine Street neighborhood, the city’s legislative body, known then as the Common Council, approved the building of Catharine Market.
As was customary, the interested parties furnished the grounds and construction costs. In subsequent decades, local and municipal funds were used to expand the facilities. This blend of local initiative and government response created a successful public market to serve as a community anchor and supply the provisioning needs of a working-class district.
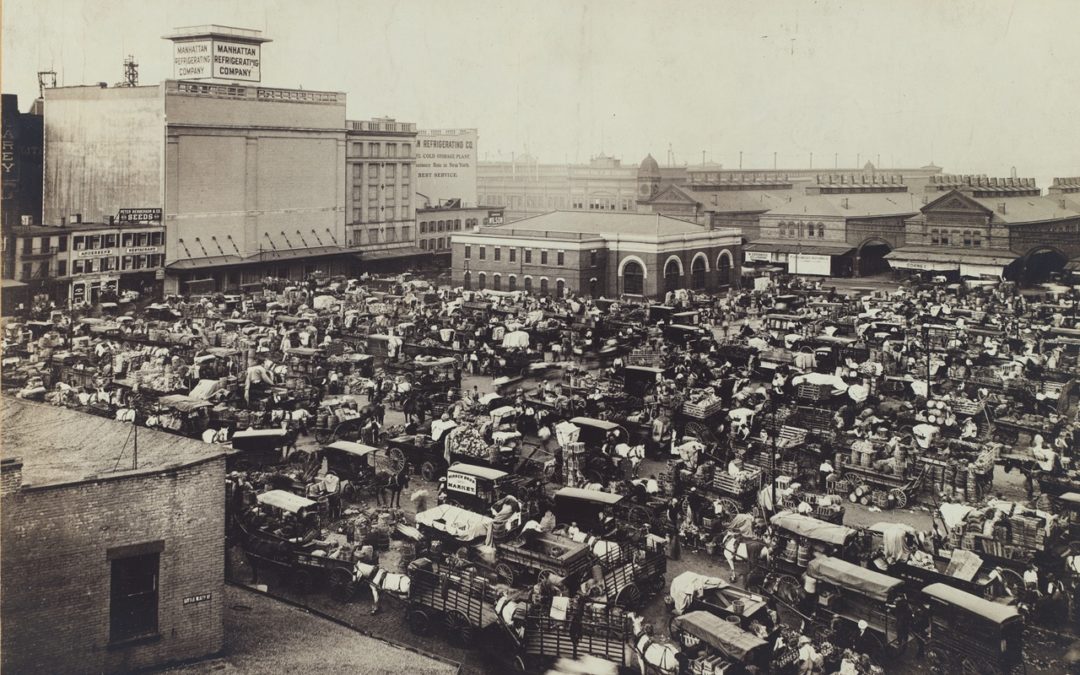
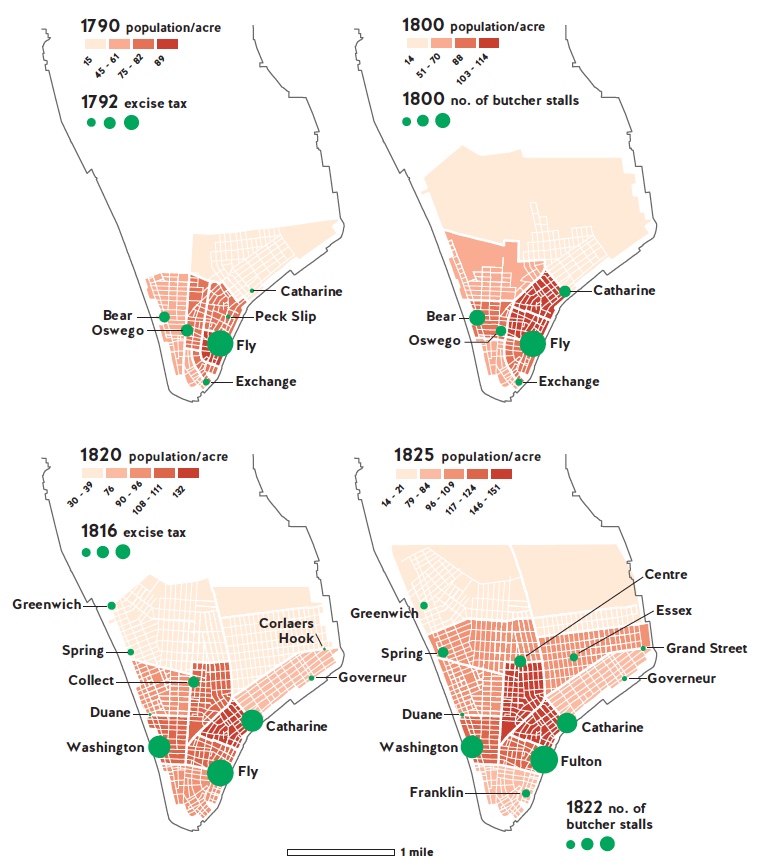
By the late 1810s, Catharine Market — located in lower Manhattan, east of where the Brooklyn Bridge now stands — became one of New York’s most abundant fresh food emporia. Its 47 butchers, 25-plus fishmongers, more than 61 regular farmers and dozens of hucksters and informal vendors, as well as the many grocers who settled nearby, supplied an estimated 25,000 people. Depending on the season and day of the week, 2,000 to 5,000 shoppers visited each day.
Catharine Market was part of a tightly regulated system, which mandated that fresh food — meat in particular — could be sold only at municipally managed and owned marketplaces. As the population exploded from 30,000 to 160,000 between 1790 and 1825, the city responded by expanding the system from six to 11 neighborhood markets.
The market infrastructure of New York in the Early Republic was a smart system in spatial terms: Its facilities reached all areas, ensuring access to supplies for all residents. No matter where one lived a market could be found within a 10-minute walk. This was a critical factor in managing an effective food distribution system when New Yorkers, lacking refrigeration, had to shop as often as twice per week in the winter and up to six times per week in the abundant summer months.
Negotiations between vendors, customers and municipal officials ensured that the markets’ capacity and volume of trade closely corresponded with their neighborhoods’ population size, indicating a match between supply and demand. Overall, the Early Republican model of public markets responded to local demands about opening new markets or upgrading existing ones, and it cost little. Through its collection of fees — excise taxes at the beginning and rents later — the system largely paid for itself.
MANHATTAN MARKET MULTIPLICATION
Between 1790 and 1825, as the population of Lower Manhattan grew, the public markets expanded — both in size and location — to meet the needs of New York residents. No matter where one lived a market could be found within a 10-minute walk, a critical factor in managing an effective food distribution system in the burgeoning urban center.
Critically, the market system provided the city’s main line of defense for food quality. It safeguarded the wholesomeness of supplies by penalizing those who sold decaying and spoiled provisions, while also instituting standards of cleanliness in the daily conditions and practice of food sales. For example, market clerks appointed by the city government enforced quality standards and fair trade practices at each location. Given their large assembly of independent vendors, public markets enabled customers to comparison-shop for price and quality. The vendors also exerted peer pressure, working with market clerks to punish violators of market laws and to uphold their market’s reputation. Moreover, the market butchers, the city’s most elite food purveyors, were artisan tradesmen who handled their vital, perishable goods with skill and care, ensuring high-quality products. Finally, given strict licensing policies and customers’ frequent purchases, neighborhood markets fostered repeated transactions and nurtured trust between buyers and sellers.
Beyond protecting public health, the system also set a baseline of equal access to food. Whether living in wealthier central districts or poorer outlying ones, New Yorkers provisioned their households under similar institutional settings. This continued even as the city grew. Developing a new neighborhood depended on extending this municipal service, funded in part from revenues earned at larger, centrally located markets.
The system was also efficient in not wasting supplies. Markets worked six days a week, from sunrise until early afternoon, except for Saturdays when they stayed open until late evening. On Sundays, only the fish stalls were open. Before refrigeration, the main constraint was perishability, so vendors — including butchers, hucksters and fishmongers who attended the markets daily, and regional farmers from rural New York and New Jersey who came less regularly — brought only as much merchandise as they expected to sell the same day.
Choice sales occurred early in the morning. By 10 a.m., the main business of the market was done. Then poor customers came to purchase cheaper, less desirable goods. At noon, secondary traders were allowed to join in, picking up market leftovers and peddling them at discounted prices after market hours and across the neighboring streets. Waste and byproducts from the key trade of butchering were recycled by an urban economy of noxious trades plied by tanneries and makers of soap, tallow and glue.
As with smart systems today, the success of the market system of early New York depended on the flow of information between key groups. The crux of the matter was the democratic process of petitioning and negotiation. All participants — residents, vendors, city officials — had to continuously (re)negotiate the location, size, layout, building material, basic rules and daily practice of the public markets. The process facilitated communication and coordination between neighborhood-based interests and citywide policies. Despite the messy politics (thanks to fragmented and competing interests), the system worked, because it was participatory, decentralized and coordinated to deliver workable compromises for everyone concerned.
For the model to continue to work, the Common Council had to adhere to its basic principles: that access to food was a public good, that fresh provisions should be sold at publicly managed markets instead of unregulated private shops, and that market facilities should be opened and expanded in response to local needs. Delays in infrastructural investments could undermine the welfare of customers and vendors, potentially jeopardizing the model’s integrity.
Indeed, from the 1830s, the system showed signs of malfunction. Demographic growth, a rising free-market ideology and weakened municipal commitment resulted in inadequate infrastructural expansion. First, unlicensed food sales outside of the municipal markets by street vendors and in private shops increased, chipping away from public market trade. As municipal spending priorities shifted, market construction came to a halt by 1837, leaving urbanizing northern districts without market facilities. In 1843, the city deregulated the food economy, allowing retailers to set up shops anywhere and without much regulatory oversight.
By mid-century, New York’s once-famous public markets were in tatters. Urbanization posed an enormous challenge — the population had skyrocketed to 500,000 by 1850. Yet instead of modernizing the market system, city officials turned to private enterprise to organize food access. Existing markets survived, but the earlier model of public market provisioning disintegrated.
In our own age of heightened debate about the role of government and private enterprise, it is worth recalling that American cities, New York especially, once depended on public market systems to feed their populations. By bringing the trade of life’s necessities under tight municipal regulation and oversight, and balancing the interests of customers and vendors, early New York managed a smart and successful market system that sustained the common good of access to food to all residents.
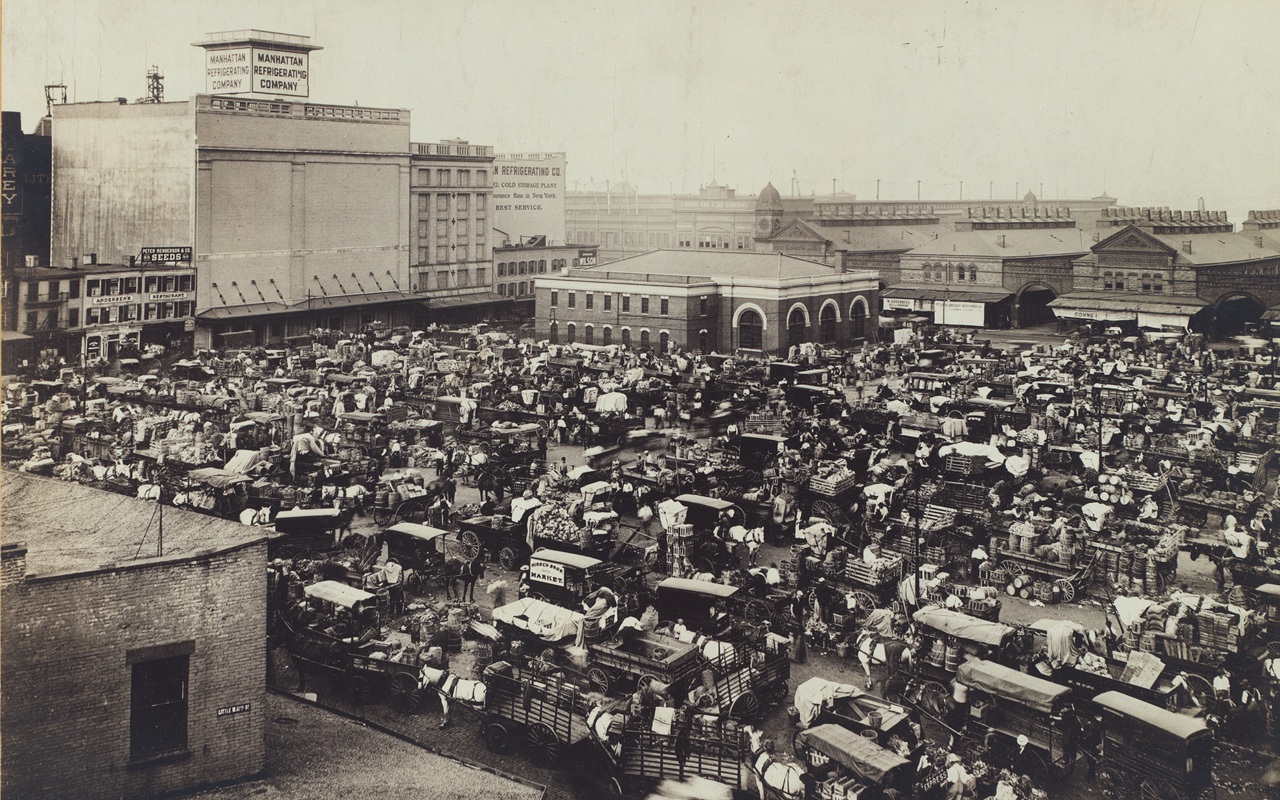

The Manhattan Refrigeration Company towers over the Gansevoort Market. The company, incorporated in 1894, operated nine cold storage warehouses. By 1906, a network of underground pipes connected the chilled warehouses, providing storage for shipments of perishable food that arrived on the steamers docked at the Chelsea and Gansevoort Piers nearby. “Mechanical refrigeration” was a new invention then. It situated the market as an area for food distribution–related businesses.
Now known as the Gansevoort Market Historic District, this space in today’s Meatpacking District was a food market throughout the 19th century. Near the Hudson River commercial waterfront, Gansevoort Market was ideally situated to transfer meat, dairy and produce from ships to the market and beyond. After the Civil War, the market space expanded and included Skelly & Fogarty’s Centennial Brewery on West 14th Street.
Buyers and sellers of regional produce and dairy also transacted their business there. In 1893, the New York Biscuit Company, which became Nabisco, added to the food-related business that crowded around the market space. You can imagine the combined aromas of manure and biscuits filling the streets.
The Gansevoort Market (1880 to 1928) has always been a mixed-use space, as you can see from this photograph taken in 1900. Low Italianate structures exist next to tall warehouses. Some of the metal canopies built for the transfer of meat into those warehouses still exist, as does some Belgian block paving. The Hudson River Railroad freight yards nearby provided transit for meat and other food items uptown and beyond Manhattan. Beginning in 1869, Cornelius Vanderbilt owned the rail line, along with the New York Central, and expanded the rail network to reach meatpackers in Chicago.
By 1880, other food markets in New York had fallen into disrepair, and vendors filling the streets had become a nuisance to pedestrians and horse-drawn vehicles. The city decided to create a new market space in the Gansevoort neighborhood to aggregate the commerce of farmers, buyers and sellers into one space. Originally developed for the sale of fruits and vegetables, Gansevoort eventually became the center of the meat market.
Horses transported most of the food from the piers and through the market. Buyers brought their wagons into the market, bringing filth and congestion with them. By 1900, almost 170,000 horses filled Manhattan’s streets. Over 250 slaughterhouses and meatpacking companies filled the Gansevoort Market neighborhood, adding to the stench and manure.


 MULTI-PURPOSE FOOD (MPF)
MULTI-PURPOSE FOOD (MPF)





 Need a refresher on how to play Kick the Can?
Need a refresher on how to play Kick the Can?